SEO or search engine optimisation is one of the least understood topics in the world of digital marketing.
Most marketers and business owners wrongly assume that they need to have a technical background to grasp SEO fully.
Nothing can be further from the truth as with a little bit of effort even a non-technical person with no prior experience of coding can understand SEO and use his knowledge to get higher rank for his website on search engine results page.
It’s quite natural that most beginners will have some doubts and questions about SEO especially if they lack any prior experience in this field.
So, in this article, we will discuss 10 most common FAQs about SEO which most people have.
1) What is SEO?
SEO refers to the process of optimising your website and webpages to get a higher rank on search engine results pages or SERPs.
Overall the medium is focused on several techniques and best practices which are essential for getting a higher position in organic search results on Google.
SEO often includes creating search optimised content using appropriate keywords, backlinking, and on-site SEO.
Search engines use algorithms to deliver the most relevant results to the searchers. SEO aims to optimise a website or webpage so that the site in question can rank higher for its main keywords.
2) What is the difference between SEO, PPC, and SEM?
SEO, PPC, and SEM are related concepts which are often confused for one another.
We’ve explained SEO above and would like to add that SEO is mostly free of cost as a person is not required to spend anything, although it needs a good amount of time and effort as an SEO campaign can take months before you will start seeing the results of it.
PPC or pay per click advertising also allows you to get a ranking in SERPs, although you will have to pay for running your ads on SERPs as the name PPC itself suggests that it’s a paid form of advertising.
Google AdWords is the leading PPC platform which allows users to show their ads above organic search results on SERPs for keywords or queries of their choice.
PPC mainly uses a bidding model where an advertiser must bid for getting a place on SERPs and usually the person with the highest bid gets the top-most rank on SERPs.
It must be noted that PPC ads which are shown on SERPs mention the fact that they are advertisements and a user can easily differentiate between PPC ads and organic search results displayed on SERPs.
SEM refers to search engine marketing which includes both the SEO and PPC.
So, SEO+PPC are collectively referred to as SEM (Search Engine Marketing), although it’d not be correct to use SEO or PPC interchangeably with SEM as they are just 2 individual elements of SEM.
3) SEO vs PPC?
SEO vs PPC is perhaps the age-old debate in the world of search engine marketing and this question has been asked numerous times since the advent of search engines.
Many people wrongly assume that they can compare these two methods of marketing when comparing SEO with PPC is like comparing apples with oranges.
SEO and PPC are two different methods of search marketing which fulfil specific needs. SEO is aimed at getting free of cost, organic traffic from search engines, whereas PPC is a paid method of advertising.
SEO takes time to deliver return on your investment, where PPC can deliver instant results.
For a person running a website, it comes down to budget, timeframe, and needs as some business owners focus on both SEO and PPC for getting targeted traffic from search engines.
4) What is On-Page SEO?
On-Page SEO refers to the practice of optimising individual web-pages to get higher ranks in search engine results pages or SERPs.
This process is primarily focused on optimising the title tag using a keyword, subheadings using H1, H2, and H3 tags, outbound and inbound links, and SEO friendly webpage URLs.
5) How is SEO changing?
SEO has undergone several changes since its inception, as search engines update their search algorithms regularly.
Google introduced several changes in its algorithm with numerous updates during the past decade, and these algorithm updates have fundamentally changed SEO.
Google’s Panda, Penguin, and Hummingbird updates can be considered as landmark changes in SEO. These updates impacted several websites both large and small as Google punished sites using duplicate content, or black-hat SEO tricks.
Another notable change in SEO is the increasing importance of social media signals as nowadays, almost every major search engine considers the popularity of a website on social media to calculate it’s rank on SERPs.
Check out our guide to the ‘How has SEO changed in the last few years?‘
6) What is Keyword Research?
Keyword research refers to the practice of identifying keywords relevant to a website as SEO and PPC both revolve around keywords.
Keywords are central to how a search engine works as anything for which a user searches using a search engine is a keyword.
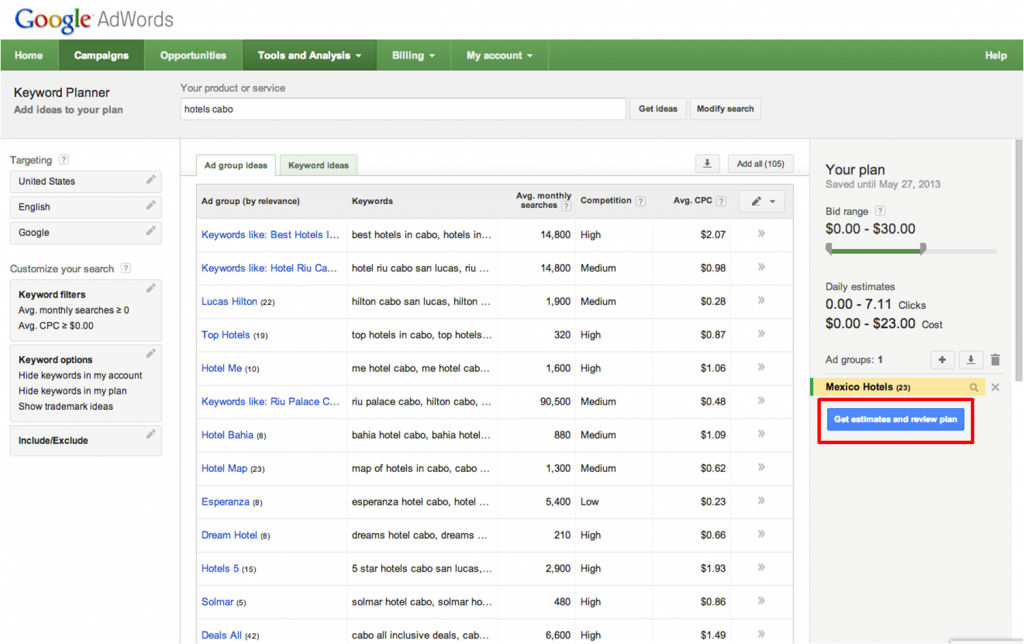
SEO campaigns are constructed around keywords, so it’s essential to have a list of relevant keywords. Marketers use several tools such as the Google AdWords Keyword Planner tool to research keywords.
During keyword research, you can also identify alternative or similar keywords which may have a low level of competition as often most valuable keywords have a high amount of competition which makes optimising your website for these keywords difficult.
Check out our guide to the ‘best SEO tools for keyword research‘
7) Is blogging beneficial for SEO?
Blogging helps in improving a website’s SERP ranking in the long run due to several reasons.
Search engine loves fresh content and blogging allows you to create keyword rich, and relevant content regularly which is then indexed by search engines.
Blogging also allows you to get high-quality backlinks from relevant sites within your industry as having a high number of useful and engaging webpages automatically increases your chances of getting backlinks from other high-quality sites.
Blogging also keeps people longer on your site and increases the average duration of a visit which is considered a positive signal by Google and other search engines.
You can also target long-tail keywords with your blog and can incorporate long-tail keywords within your blog posts to increase your chances of getting a higher SERP ranking.
Check out our guides to ‘Evergreen blog content‘ and ‘Blogging as a Travel Businesses – Why it is Essential for Growth!‘
8) Are meta tags still important for SEO?
There was a time when meta tags were the craze in the world of SEO, and almost all webmasters were busy adding meta tags to their webpages.
Then, in 2009, Google announced that they no longer use meta tags for ranking webpages in their search engine results pages or SERPs. This changed the perception of meta tags in the eyes of SEO practitioners, and their use declined dramatically.
Many webmasters and SEO professionals still consider them essential for SEO, although no search engine apart from Yandex uses meta tags for ranking websites on SERPs.
Although, it’s still a good idea to use meta tags as these tags influence how your site is displayed in search results and may also affect the number of visitors which you can get from SERPs.
You can consider using Title, Description, and Keywords meta tags as these 3 are the most commonly used meta tags. It’s okay even if you don’t use meta tags as they are no longer used for ranking webpages. So, they only serve an aesthetic purpose.
9) What are backlinks and how they are important for SEO?
Backlinks are links from other websites which point towards your site.
Backlinks are quite crucial for SEO as the internet is built using external links and they remain crucial to understanding the relationship between websites and pages.
We browse sites after clicking a backlink which we may find in our social media stream, any other website or blog or at any other source.
Search engines give higher ranks in SERPs to websites which have a large number of quality backlinks from relevant sites in their industry. Backlinks are also important for search engine indexing as search spiders use these links to index your site in their database.
Backlinks are essential for the reputation and credibility of your website, and they also remain the most potent method of driving traffic to your site.
A single backlink from a reputed website which has a high userbase can give a new lease of life to your site as there are cases when a website got thousands and hundreds of thousands of visitors from a single backlink from a widely read website such as BBC or NYtimes.com.
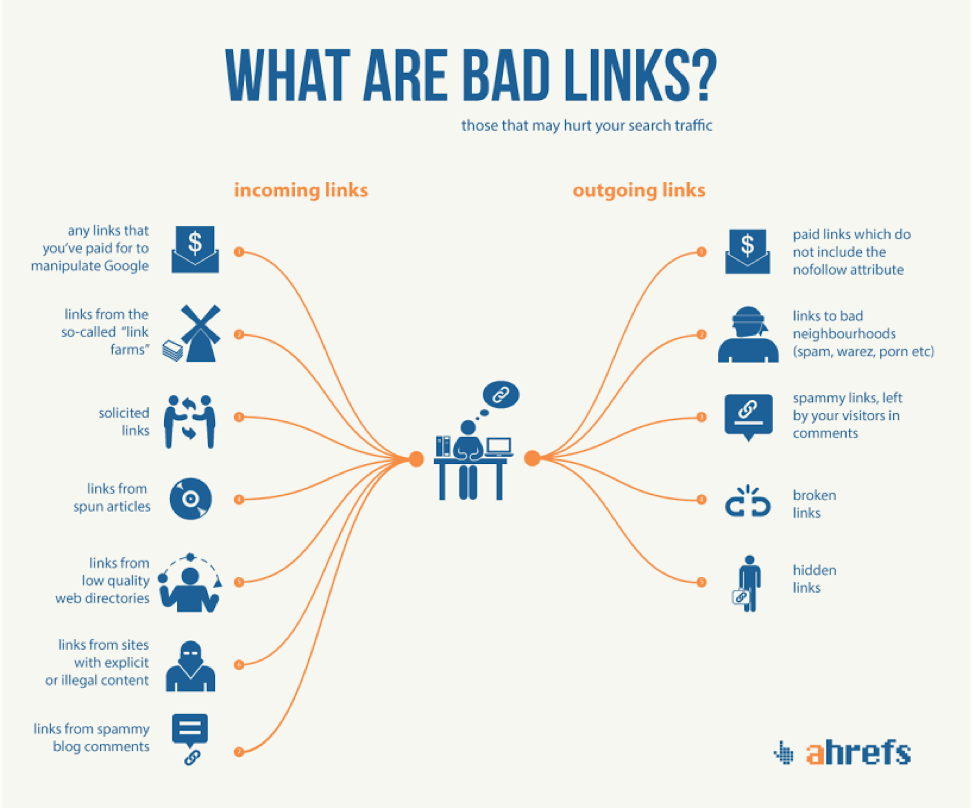
It’s also important to note here that search engines frown on paid links and you must not pay to get a backlink to your website.
If Google finds out that you’ve bought backlinks for your website, then your site may be penalised by Google and may lose it’s ranking on SERPs along with a significant amount of traffic.
So, you must always earn backlinks instead of buying them from link marketplaces as such tactics no longer work, and often cause more harm than good.
Check out our guide to ‘the importance of links for travel businesses‘
10) What is Link Equity or Link Juice?
Search engines use backlinks to gather information about websites, and it’s assumed that certain types of links pass value and authority from one page to another.
The concept of Link Equity is closely linked with PageRank, which was the first and original algorithm used by Google to rank websites on their search engine results pages.
Google considers several factors when calculating the link equity such as the type of link, the authority of the linking site, relevancy of the link, following status of the link (do-follow link), the total number of outgoing links from a webpage, https status of the linked page etc.
Link equity can be controlled by using a do-follow or no-follow link. A webmaster may also choose to tell search engine’s crawler to ignore a link by using a robots.txt file and in this case also no link equity will be passed to the linked page.